Table of Contents
- US inflation still stubbornly high despite August slowdown | AP News
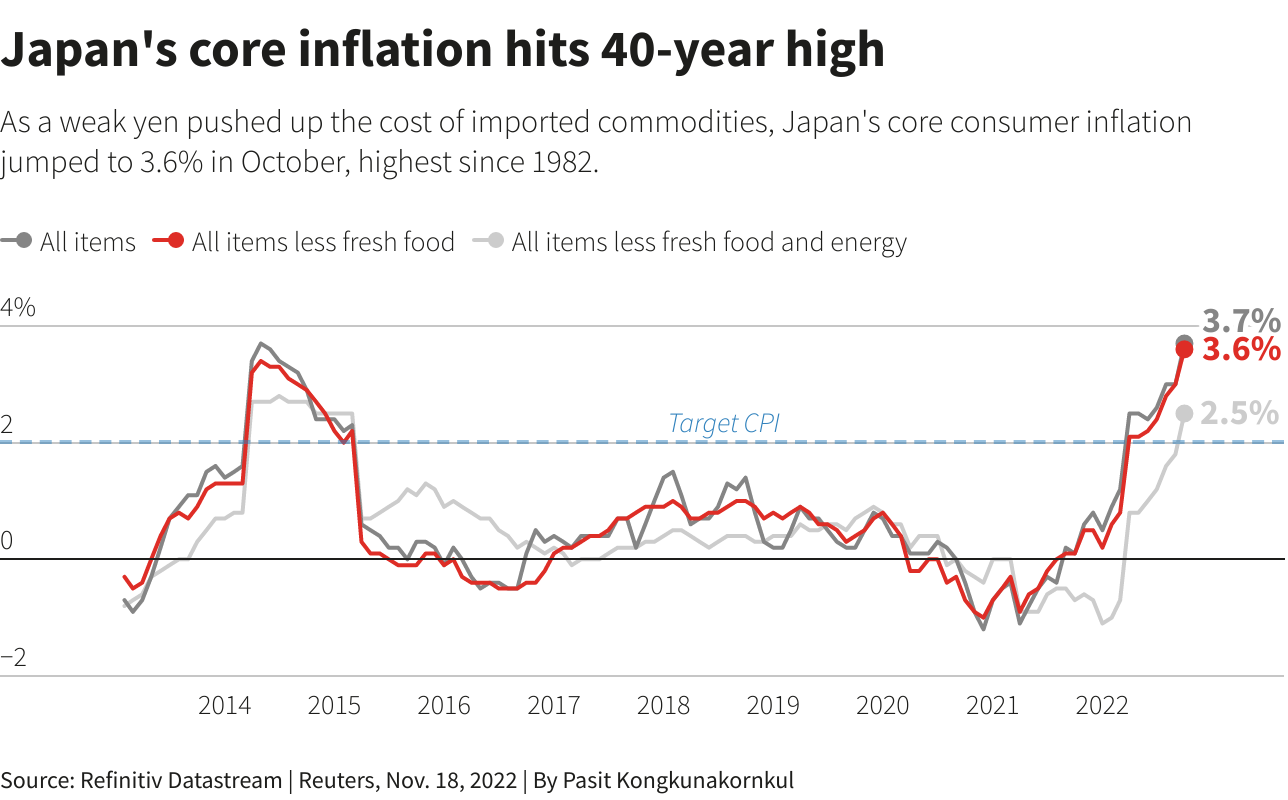
- Japan Inflation Rate July 2024 To June 2024 - Nissa Leland
- Inflation increases as Biden keeps bragging about his spending
- 14 charts that explain America’s inflation mess
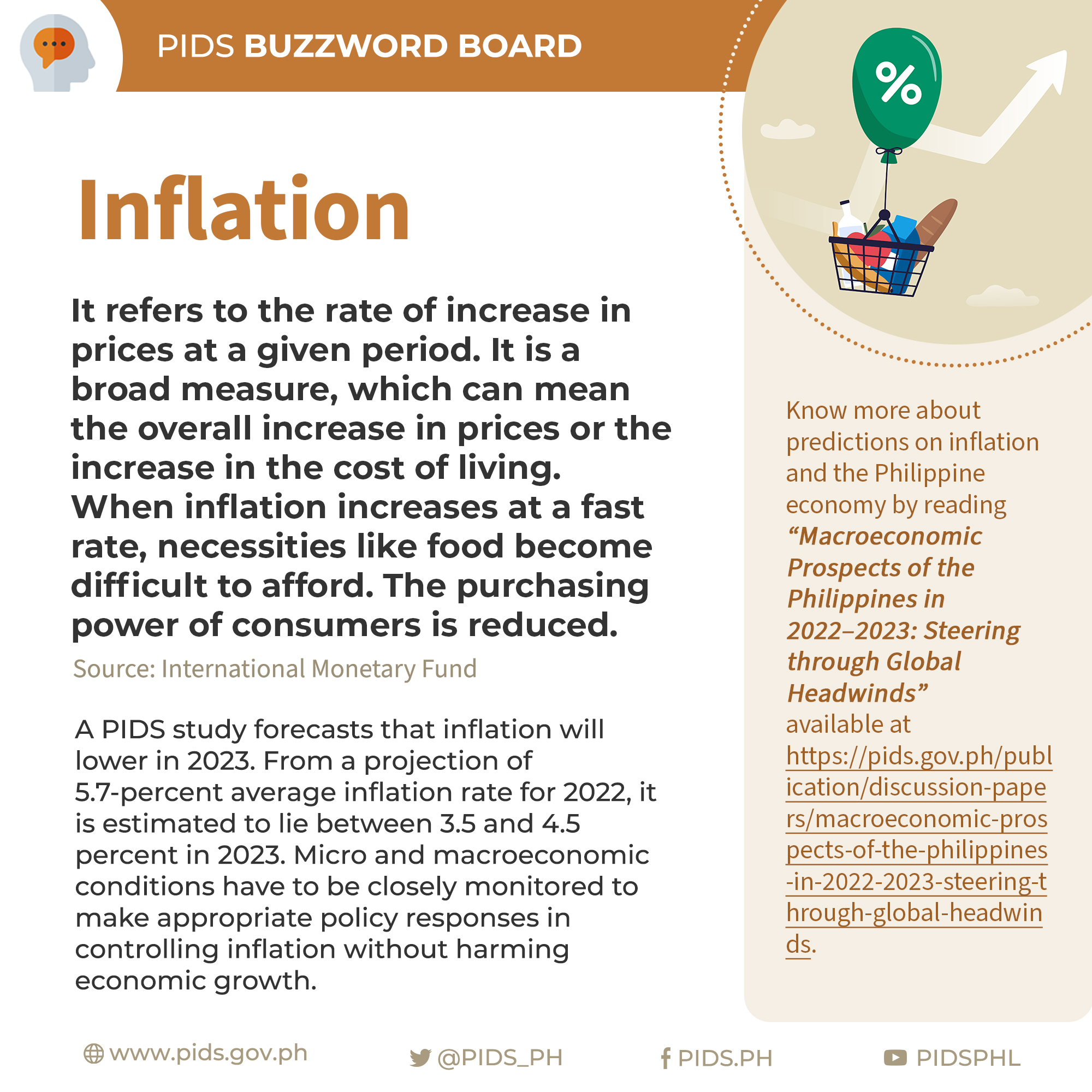
- PIDS - Philippine Institute for Development Studies
- US inflation below 5% for first time in two years
- US inflation: US inflation hits two-year low; declines sharply to 3% in ...
- New inflation data shows prices continue to rise
- Inflation Cools to 5% in March, but It’s a Long Road Back to Normal ...
- US Inflation at its highest level in 40 years


The tariffs imposed by the Trump administration on imported goods from countries such as China, Mexico, and Canada have led to higher prices for consumers and businesses. The tariffs have also sparked fears of a trade war, which could have far-reaching consequences for the global economy. However, Waller believes that the inflationary effects of tariffs will be temporary, citing the fact that the prices of goods subject to tariffs are already beginning to decline.
Waller's comments are in line with the views of other Federal Reserve officials, who have also downplayed the risks of tariff-driven inflation. The Fed has been keeping a close eye on inflation, which has been running below its 2% target in recent months. While the tariffs have led to higher prices for some goods, the overall inflation rate has remained relatively stable. According to Waller, the Fed is more concerned about the potential impact of tariffs on economic growth, rather than inflation.


What are Tariffs and How Do They Affect Inflation?


In the case of the United States, the tariffs imposed on imported goods from countries such as China have led to higher prices for goods such as electronics, furniture, and clothing. However, the impact of tariffs on inflation has been relatively modest, with the overall inflation rate remaining below the Fed's 2% target. According to Waller, the inflationary effects of tariffs are likely to be short-lived, as businesses and consumers adjust to the new trade landscape.

Implications of Transitory Tariff Inflation

In conclusion, Fed Governor Christopher Waller's comments on tariff inflation are reassuring, suggesting that the price increases resulting from tariffs will be short-lived. While the tariffs have led to higher prices for some goods, the overall inflation rate has remained relatively stable. As the trade tensions between the United States and its trading partners continue to evolve, it is essential to monitor the impact of tariffs on inflation and economic growth. The Fed's stance on tariff inflation will be critical in shaping monetary policy and supporting the economy in the coming months.
Note: This article is for general information purposes only and should not be considered as investment advice. The views expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views of any organization or institution.